Blog de Artículos
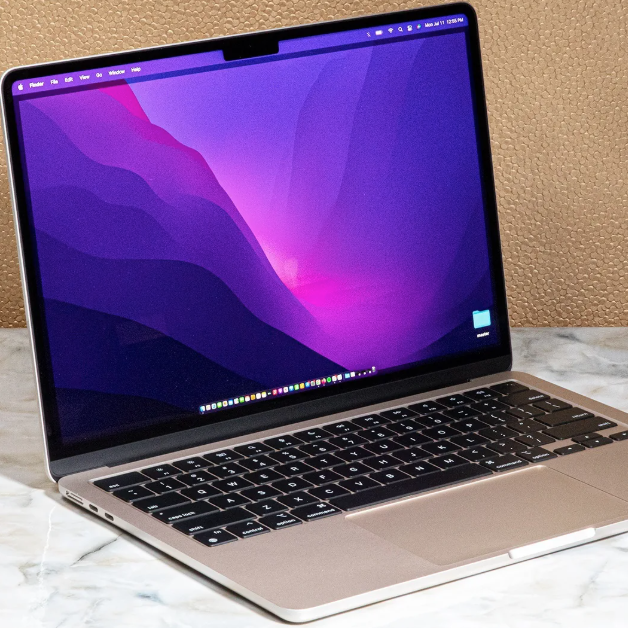

Profile and History of The MacBook Pro
The MacBook Pro is a line of computers developed and manufactured by Apple. Introduced in 2006, it is the high-end sibling of the MacBook family, sitting above the ultra-portable MacBook Air and previously the low-end MacBook line.
It is currently sold with 14-inch and 16-inch screens, all using Apple M-series chips. Before Apple silicon, the MacBook Pro used Intel chips, and was the first laptop made by Apple to do so, replacing the earlier PowerBook. It was also the first Apple laptop to carry the MacBook moniker.

Profile and History of The MacBook Air
The MacBook Air is a line of Mac laptop computers developed and manufactured by Apple since 2008.
It features a thin, light structure in a machined aluminum case and currently either a 13-inch or 15-inch screen.
The MacBook Air's lower prices relative to the larger, higher performance MacBook Pro have made it Apple's entry-level notebook since the discontinuation of the original MacBook line in 2012.

Profile and History of The MacBook
The MacBook is a brand of Mac laptop computers developed and marketed by Apple that use Apple's macOS operating system since 2006.
The MacBook brand replaced the PowerBook and iBook brands during the Mac transition to Intel processors, announced in 2005.
The current lineup consists of the MacBook Air (2008–present) and the MacBook Pro (2006–present).
Two different lines simply named "MacBook" existed from 2006 to 2012 and 2015 to 2019. The MacBook brand has been the "world's top-selling line of premium laptops" for many years.
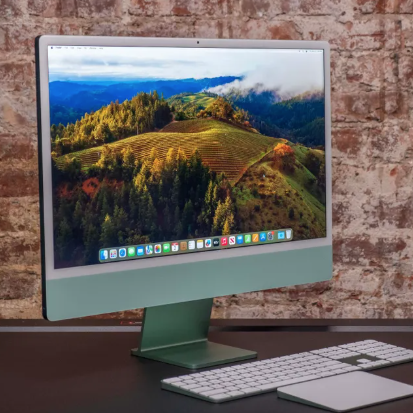

Profile and History of the iMac
The iMac is a series of all-in-one computers from Apple Inc., sold as part of the company's Mac family of computers.
First introduced in 1998, it has remained a primary part of Apple's consumer desktop offerings since and evolved through seven distinct forms. The iMac natively runs the macOS operating system.
The design of the iMac has been seen as both controversial and trendsetting. From its introduction, the computer has eschewed many entrenched legacy technologies, notably becoming an early adopter of the USB port, and removing floppy disk and later optical disc drives.
The most recent revision, the Apple Silicon iMac, uses Apple's own processors (silicon) and is 11.5 millimeters (0.45 in) thick.
Between 2017 and 2021, Apple also sold a workstation-class version of the computer called the iMac Pro.
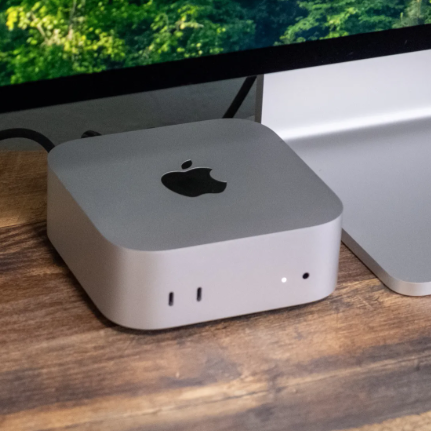

Profile and History of the Mac Mini
The Mac Mini (stylized as Mac mini) is a small form factor desktop computer developed and marketed by Apple Inc.
It is one of the company's four current Mac desktop computers, positioned as the entry-level consumer product, below the all-in-one iMac and the professional Mac Studio and Mac Pro.
From its launch, the device has been sold without a display, keyboard, or mouse, and was originally marketed with the slogan "BYODKM" (Bring Your Own Display, Keyboard, and Mouse).
This strategic pitch targeted current owners of Windows desktop computers; by leveraging peripherals users likely already owned, the computer offered a cost-effective way to switch to a Mac.

Profile and History of the Mac Pro
The Mac Pro is a series of workstations and servers for professionals made by Apple Inc. since 2006.
The Mac Pro, by some performance benchmarks, is the most powerful computer that Apple offers.
It is one of four desktop computers in the current Mac lineup, sitting above the Mac Mini, iMac and Mac Studio.
Introduced in August 2006, the Mac Pro was an Intel-based replacement for the Power Mac line and had two dual-core Xeon Wood-crest processors and a rectangular tower case carried over from the Power Mac G5.
It was updated on April 4, 2007, by a dual quad-core Xeon Clovertown model, then on January 8, 2008, by a dual quad-core Xeon Harpertown model.
Revisions in 2010 and 2012 revisions had Nehalem-EP/Westmere-EP architecture Intel Xeon processors.
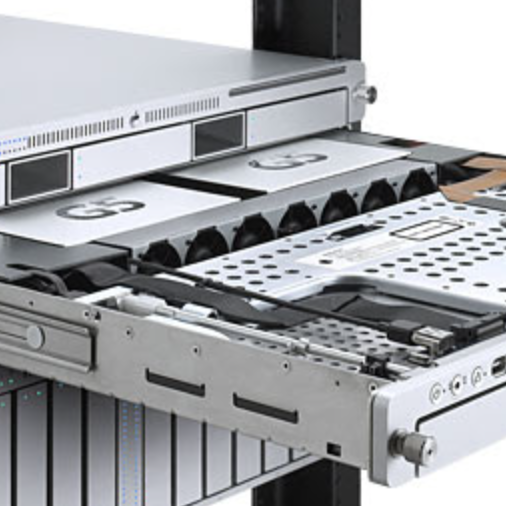

Profile and History of the Mac Xserve
The Xserve is a discontinued series of rack-mounted servers that was manufactured by Apple Inc. between 2002 and 2011.
It was Apple's first rack-mounted server, and could function as a file server, web server or run high-performance computing applications in clusters – a dedicated cluster Xserve, the Xserve Cluster Node, without a video card and optical drives was also available.
The first Xserve had a PowerPC G4 processor, replaced by a PowerPC G5 in 2004, and by Intel Xeon processors in 2006; each was available in single-processor and dual-processor configurations.
The Xserve was discontinued in 2011, and replaced with the Mac Pro Server and the Mac Mini Server.
Before the Xserve, Apple's server line included the Apple Workgroup Server, Macintosh Server, and Apple Network Server
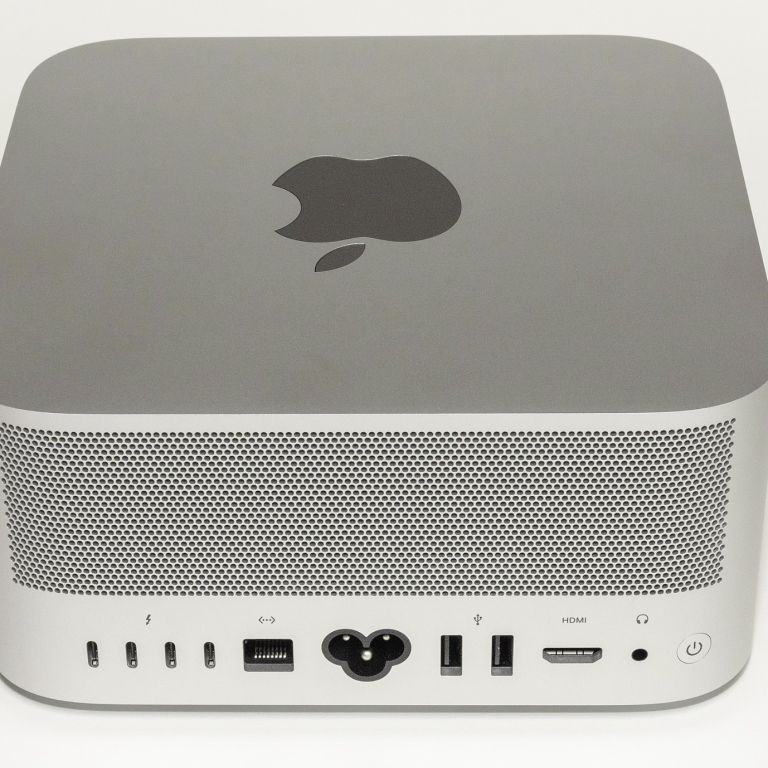

Profile and History of the Mac Studio
The Mac Studio is a desktop personal computer, designed to sit between the consumer-level Mac Mini and the professional-targeted Mac Pro.
The Mac Studio has an identical width and depth to the contemporary Mac mini, 7.7 inches (200 mm), but is stands taller at 3.7 inches (94 mm).
The Mac Studio was initially offered in two ARM-based SoC: the M1 Max or the M1 Ultra, which combines two M1 Max chips in one package.
It has four Thunderbolt 4 (USB 4) ports, two USB 3.0 Type-A ports, HDMI (up to 4K @ 60 Hz), 10Gb Ethernet with Lights Out Management and a headphone jack. The front panel has two USB-C ports (Thunderbolt 4 in M1 Ultra models) and an SD card slot (that supports SDXC cards and UHS-II bus), making it the first desktop Mac since the 2012 Mac Pro to have I/O on the front.
It is cooled by a pair of double-sided blowers and a mesh of holes on the bottom and back of the case, which helps reduce the noise of fans spinning.

The Time-Line of All Apple Products
This timeline of Apple products is a list of all computers, phones, tablets, wearables, and other products made by Apple Inc. This list is ordered by the release date of the products.
Macintosh Performa models were often physically identical to other models, in which case they are omitted in favor of the identical twin.
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to a type of apple called McIntosh.
The current product lineup includes the MacBook Air and MacBook Pro laptops, and the iMac, Mac Mini, Mac Studio, and Mac Pro desktops.
Macs are currently sold with Apple's UNIX-based macOS operating system, which is not licensed to other manufacturers and exclusively bundled with Mac computers.
This operating system replaced Apple's original Macintosh operating system, which has variously been named System, Mac OS, and Classic Mac OS.
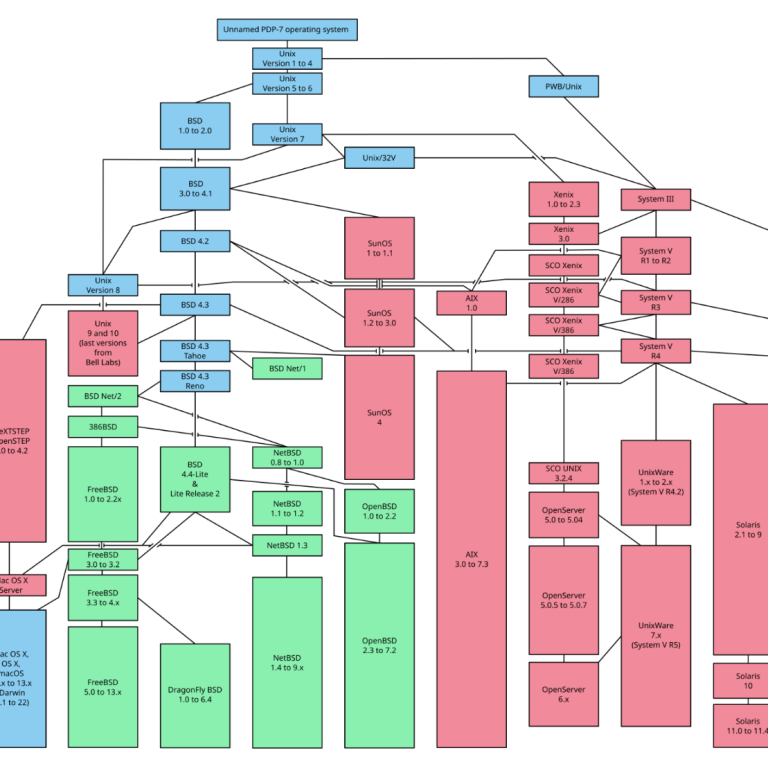
The Time-Line of All Mac OS Operating Systems
The history of macOS, Apple's current Mac operating system formerly named Mac OS X until 2011 and then OS X until 2016, began with the company's project to replace its "classic" Mac OS.
That system, up to and including its final release Mac OS 9, was a direct descendant of the operating system Apple had used in its Mac computers since their introduction in 1984.
However, the current macOS is a UNIX operating system built on technology that had been developed at NeXT from the 1980s until Apple purchased the company in early 1997.
MacOS components derived from BSD include multiuser access, TCP/IP networking, and memory protection.
Although it was originally marketed as simply "version 10" of Mac OS (indicated by the Roman numeral "X"), it has a completely different codebase from Mac OS 9, as well as substantial changes to its user interface.
The transition was a technologically and strategically significant one. To ease the transition for users and developers, versions 10.0 through 10.4 were able to run Mac OS 9 and its applications in the Classic Environment, a compatibility layer.
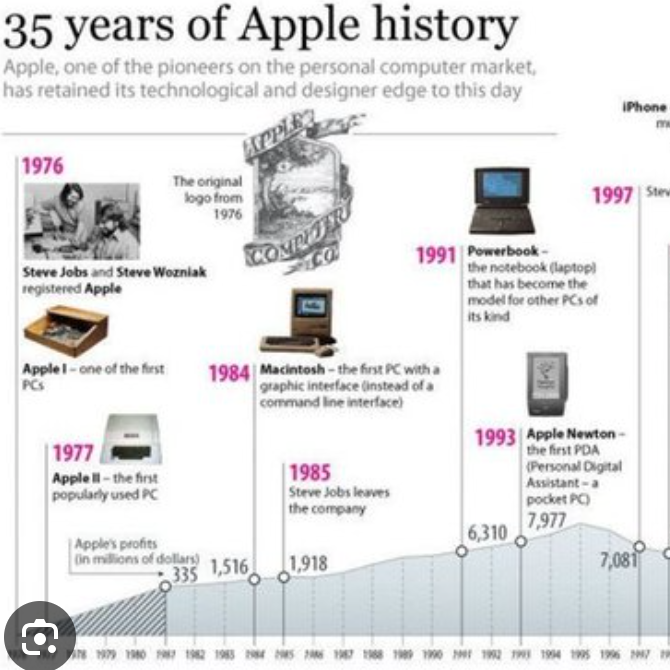
The Time-Line and History of Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services.
Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Company by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne, the company was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. the following year.
It was renamed Apple Inc. in 2007 as the company had expanded its focus from computers to consumer electronics.
Apple is the largest technology company by revenue, with US$391.04 billion in the 2024 fiscal year.
The company was founded to produce and market Wozniak's Apple I personal computer.
Its second computer, the Apple II, became a best seller as one of the first mass-produced microcomputers.
Apple's product lineup includes portable and home hardware such as the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, Mac, and Apple TV; operating systems such as iOS, iPadOS, and macOS; and various software and services including Apple Pay, iCloud, and multimedia streaming services like Apple Music and Apple TV+.

All About Planned Obsolescence
In economics and industrial design, planned obsolescence (also called built-in obsolescence or premature obsolescence) is the concept of policies planning or designing a product with an artificially limited useful life or a purposely frail design, so that it becomes obsolete after a certain predetermined period of time upon which it decrementally functions or suddenly ceases to function, or might be perceived as unfashionable.
The rationale behind this strategy is to generate long-term sales volume by reducing the time between repeat purchases (referred to as "shortening the replacement cycle").
It is the deliberate shortening of the lifespan of a product to force people to purchase functional replacements.
Planned obsolescence tends to work best when a producer has at least an oligopoly.Before introducing a planned obsolescence, the producer has to know that the customer is at least somewhat likely to buy a replacement from them in the form of brand loyalty.
In these cases of planned obsolescence, there is an information asymmetry between the producer, who knows how long the product was designed to last, and the customer, who does not.
When a market becomes more competitive, product lifespans tend to increase.[

Qué es el Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) es la versión más reciente de Google Analytics, la herramienta de análisis web de Google. Reemplaza a la versión anterior conocida como Universal Analytics (UA). GA4 ofrece una forma más avanzada y flexible de rastrear y analizar el comportamiento de los usuarios en sitios web y aplicaciones móviles.
GA4 es una plataforma de análisis que permite:
Medir el comportamiento de los usuarios en sitios web y apps. Hacer un seguimiento unificado de múltiples dispositivos (web y móviles). Usar eventos en lugar de sesiones como base del análisis (todo se mide como un evento). Obtener informes predictivos con inteligencia artificial (como probabilidad de conversión o abandono).
¿Para qué se usa?
Entender cómo los usuarios navegan por tu web o app. Analizar el embudo de conversión. Medir campañas de marketing. Tomar decisiones basadas en datos reales. Prepararse para un futuro sin cookies de terceros.
+34 910 600 687 info@allmac.eu https://allmac.eu
Necesitamos su consentimiento para cargar las traducciones
Utilizamos un servicio de terceros para traducir el contenido del sitio web que puede recopilar datos sobre su actividad. Por favor revise los detalles en la política de privacidad y acepte el servicio para ver las traducciones.